What Is Newton’s First Law Definition Examples And Applications
Newton’s First Law is a simple rule about how things move. It says that if something is not moving, it will stay still unless something pushes or pulls it. If something is already moving, it will keep moving in the same way unless a force stops it or changes its direction. This rule is also called the Law of Inertia because it explains why objects resist changes in their motion. What is Newton’s First Law helps us see why things move the way they do in everyday life.
Explore the latest trends and timeless styles at Webfreen.com Fashion
What is Newton’s First Law?
Newton’s First Law, also known as the Law of Inertia, is one of the fundamental principles of physics. It explains how objects move and how forces interact with them. This law is an essential part of classical mechanics and helps us understand motion in everyday life. But what is Newton’s First Law? Let’s explore its meaning, significance, and real-life applications in simple words.
Newton’s First Law
What is Newton’s First Law? It states that an object will remain at rest or continue to move in a straight line at a constant speed unless acted upon by an external force. In simple terms, if nothing disturbs an object, it will keep doing what it was doing. This concept is known as inertia.
Concept of Inertia
Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion. This means that objects do not change their speed or direction unless something forces them to do so. The heavier an object is, the more inertia it has. That’s why pushing a heavy box is harder than pushing a small one.
ALSO READ: The Benefits Of Plant Nurseries Webfreen.Com
| Property | Effect on Inertia |
|---|---|
| More Mass | More Inertia |
| Less Mass | Less Inertia |
| No External Force | No Change in Motion |
| Applied Force | Changes Motion |
Examples of Newton’s First Law in Everyday Life
Newton’s First Law is visible in our daily activities. Here are a few examples:
A book on a table stays there until someone moves it. If no force is applied, the book will never move.
A rolling ball slows down due to friction. If there were no friction, the ball would keep rolling forever.
Passengers in a car feel a jerk when the driver suddenly stops. The passengers keep moving forward due to inertia.
A spaceship continues moving in space without needing fuel. In the absence of external forces, it keeps traveling at the same speed and direction.
ALSO READ: 80s Black Fashion Trends Style And Culture
How Newton’s First Law Works
To understand What is Newton’s First Law, let’s break it down into two conditions:
If an object is at rest, it stays at rest. Unless someone or something moves it, it will remain in the same position.
If an object is in motion, it keeps moving. It will continue at the same speed and in the same direction unless an external force like friction or air resistance slows it down.
Forces That Can Change Motion
Even though Newton’s First Law states that an object keeps moving or stays still, real-world objects eventually stop due to external forces such as:
Friction:
The force that resists motion between two surfaces.
Gravity:
The force pulling objects towards Earth.
Air Resistance:
The force that slows down moving objects in the air.
Importance of Newton’s First Law in Science and Engineering
Newton’s First Law is essential in many fields, including engineering, aviation, and space exploration. Scientists and engineers use this principle to design vehicles, machines, and even rockets.
Car Safety:
Seatbelts protect passengers by preventing them from continuing forward in case of a sudden stop.
Sports:
Athletes use this law to predict ball movement and improve their game.
Aerospace:
Spacecraft move without needing continuous fuel because there is no friction in space.
What Is Newton’s First Law Relation with Other Laws
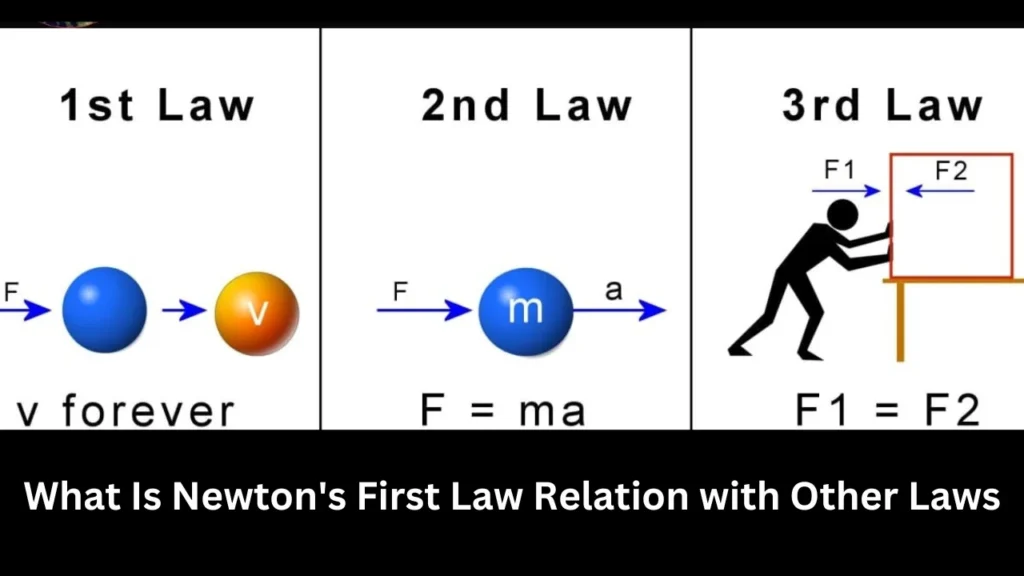
Newton’s First Law is part of Newton’s Three Laws of Motion:
| Newton’s Laws | Description |
| First Law | An object remains in its state of motion unless acted upon by an external force. |
| Second Law | Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). |
| Third Law | For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. |
Each of these laws helps explain how motion works in different situations.
Common Misconceptions About Newton’s First Law
There are several misunderstandings about Newton’s First Law. Some people think that objects naturally stop moving, but that’s not true. Objects stop due to forces like friction and air resistance, not because motion naturally ends. If friction were removed, an object would continue moving forever.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Newton’s First Law called the Law of Inertia?
It is called the Law of Inertia because it describes how objects resist changes in their motion unless acted upon by an external force.
What is an example of Newton’s First Law in daily life?
One example is when you suddenly stop your car, but your body continues moving forward due to inertia.
How does Newton’s First Law apply in space?
Since there is no air resistance or friction in space, an object will keep moving at the same speed and direction indefinitely.
What is the importance of Newton’s First Law?
It helps scientists and engineers understand motion, design safety measures, and improve transportation and aerospace technology.
Conclusion
What is newton’s first law, is a fundamental concept in physics that explains why objects stay at rest or continue moving in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also called the Law of Inertia, helps us understand motion in everyday life, from car movements to space exploration. Without external forces like friction and air resistance, objects would continue moving forever. This law plays a crucial role in science, engineering, and technology, making it one of the most important principles in physics.